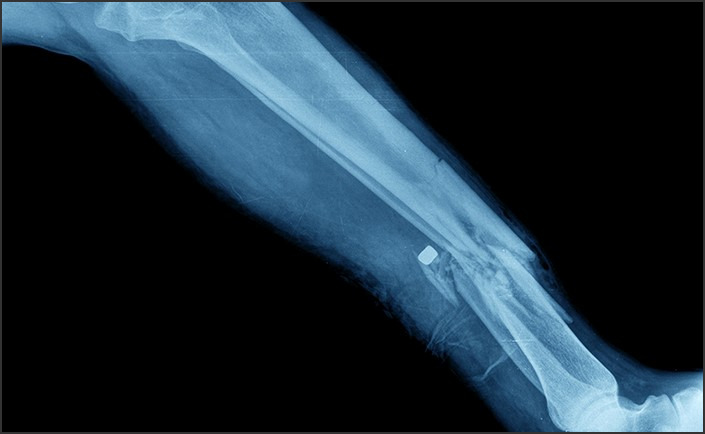
Oblique Fracture of the Distal Fibula refers to a specific type of bone break that occurs at an angle in the lower part of the fibula, one of the two bones located in the lower leg. This fracture is typically caused by a sudden, forceful impact or trauma such as a fall, a direct blow, or a twisting injury to the leg. Treatment for this type of fracture usually involves immobilization with a cast or splint, and in severe cases, surgical intervention may be required to realign the bone and facilitate healing.
Understanding Oblique Fracture of the Distal Fibula: Causes and Effective Treatment Methods
An oblique fracture of the distal fibula is a specific type of bone break that occurs in the lower part of the fibula, one of the two bones that make up the lower leg. This fracture is characterized by a diagonal break across the bone, which distinguishes it from other types of fractures such as transverse or spiral fractures. Understanding the causes and effective treatment methods for this type of fracture is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers.
The fibula, the smaller of the two bones in the lower leg, runs parallel to the tibia and plays a significant role in stabilizing the ankle and supporting the muscles of the lower leg. The distal end of the fibula is particularly vulnerable to injury due to its location and the forces exerted on it during physical activities. Oblique fractures of the distal fibula can occur due to a variety of causes, including direct trauma to the leg, such as a fall or a blow, or indirect forces, such as twisting or bending of the ankle.
High-impact sports, such as football or skiing, are common culprits, as they often involve sudden changes in direction and speed, which can put excessive strain on the fibula. Additionally, conditions that weaken the bones, such as osteoporosis, can also increase the risk of this type of fracture. It’s important to note that while anyone can suffer from an oblique fracture of the distal fibula, individuals with a higher risk are those who engage in high-risk activities or have underlying health conditions that weaken their bones.
Treatment for an oblique fracture of the distal fibula typically involves immobilization to allow the bone to heal. This is often achieved through the use of a cast or brace, which restricts movement and provides support to the injured area. In some cases, surgery may be necessary, particularly if the fracture is severe or if the bone fragments have been displaced. Surgical intervention usually involves the use of metal plates and screws to hold the bone fragments in place while they heal.
Physical therapy is also a crucial part of the recovery process. Once the bone has healed sufficiently, physical therapy exercises can help restore strength and flexibility to the affected leg. These exercises are designed to gradually increase the load on the healing bone, promoting further healing and helping to prevent future injuries.
Pain management is another important aspect of treatment. This can involve over-the-counter pain relievers, prescription medications, or in some cases, nerve blocks or other more advanced pain management techniques. It’s important for patients to work closely with their healthcare provider to develop a pain management plan that is effective and safe for them.
In conclusion, an oblique fracture of the distal fibula is a serious injury that requires prompt and appropriate treatment. Understanding the causes and treatment options can help patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions about care. With proper treatment and rehabilitation, most patients can expect to make a full recovery.Oblique fractures of the distal fibula are typically caused by indirect trauma or twisting forces applied to the ankle. This type of fracture is characterized by a diagonal break across the bone. Treatment usually involves immobilization with a cast or splint to allow the bone to heal, and in severe cases, surgery may be required. Physical therapy is often recommended post-treatment to restore strength and mobility. Therefore, it’s crucial to seek immediate medical attention following an injury to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.